WALKING TOWARDS ROBOTICS, AI and IoT

Collaborative robotics, IoT and Machine Learning/AI will lead robotics in the coming years. Collaborative robots have become the perfect ally for workers on the production line. They are support tools for operators in order to free them from repetitive and boring tasks, so they can take advantage of the time to perform other activities.
Sources: AER Automation, Propia, IFR, MarketsandMarkets and Planeta Chatbot /
www.aer-automation.com/mercados-emergentes/robotica-colaborativa/
Digitization, Industria 4.0 and Intelligent Production. The name varies internationally, but the central idea remains the same. What it proposes is nothing less than a long-term transformation of the world's perception of industrial production through the seamless connection of the digital and real worlds.
Complete digitization of networked processes, innovative business models, new processes and materials will make it possible to manufacture products in a much more flexible, energy-efficient, resource-saving way and with a high level of customization.
The rapid advance of robotics will permanently change the world, just as the Internet has already done. Today, robots are a key element of Industria 4.0, they provide answers, with new production methods, to the main questions of our times.
What is a collaborative robot?
Collaborative robots are designed to perform tasks in collaboration with human workers. The International Federation of Robotics defines two types of collaborative robots:
- A first group includes robots designed for collaborative use that comply with ISO 10218-1, which specifies the requirements and guidelines for safe design, protective measures and usage information.
- A second group includes robots designed for collaborative use that do not comply with ISO 10218-1. This does not mean that these robots are not safe, since they can follow different security standards, for example, national standards.
- The so-called "cobots" are designed with a series of technical features that ensure the safety of a worker when he comes into direct contact with the robot, either deliberately or by accident. These features include lightweight materials, rounded contours and sensors at the base of the robot or at the joints that measure and control force and speed and ensure that defined thresholds are not exceeded in the event of contact.
Human-Robot Collaboration
- Far from re-employing human workers, robots improve their productivity, freeing them from monotonous and repetitive tasks and allowing them to focus on more complex tasks or finish the task in collaboration with the robot in a shared space. Workers are more willing to accept the introduction of a collaborative robot in their work environment because they see them as tools that help them and make their work easier and not as a technology that will replace them. It's like working "with a partner", with unlimited possibilities.
- In a collaborative environment, a staff provides skill, flexibility and the ability to solve problems, while a collaborative robot provides strength, endurance and precision in performing the task at hand.
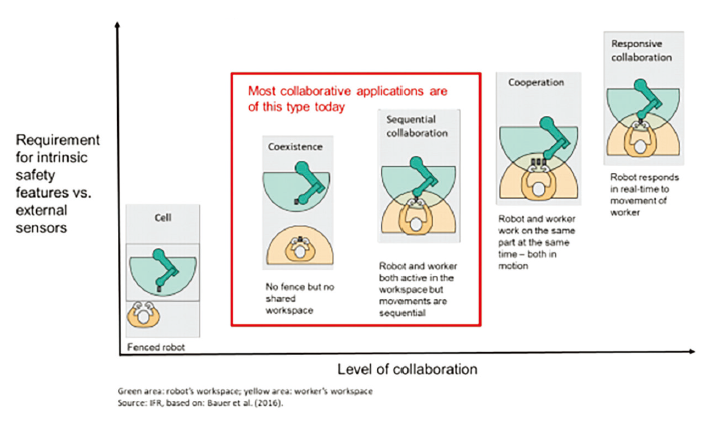
- Currently the most common collaborative applications are shared workspaces, but other situations occur (see picture 1).
Picture 1. Types of collaboration with industrial robots
Collaborative robots provide cost-effective access to industrial automation. They allow to automate parts of a production line with minimum changes with respect to the rest of the line providing to the SMEs -- that are not automated -- the option to be able to adopt these technologies. This means access to a market that represents 99% and where traditional industrial robots have not been able to penetrate. The programming of "cobots" is increasingly simple and intuitive and offer maximum flexibility for the robot to execute a function different from the previous one. They are lightweight and can be easily moved around the factory.
Future Trends
The collaborative robotics market is still in an initial phase with a high projection of future. End users and system integrators are still gaining experience in designing and implementing collaborative applications. Technological advances in sensors and grippers hold promise for expanding the range of actions the robot can perform. The programming advances to be more and more intuitive, not only for cobots but also for traditional industrial robots.
An unprecedented growth
According to the information published by the MarketsandMarkets portal, we are looking at a market of 710 million dollars that will grow to over 12,303 million in 2025, which implies a compound annual growth rate of 50.31%. These figures include all the collaborative robots both by payload capacity (up to 5 kg, between 5 and 10 kg, above 10 kg), by sector (automotive, electronics, metal, plastic and rubber, food and beverage or health), applications and geographies.
According to the analysts, this great growth responds to the high rate of return of investment and the low price of the collaborative robots, which results in the great adoption of robots on the part of the SMEs, the increase of the investments in automation to support the evolution of Industria 4.0, the improvement of the man-machine interface (HMI) and the increase of the AI capacity to imitate human behavior.
By use cases, the "pick and place" application represents the majority of the world market for collaborative robots. However, analysts believe that assembly applications will grow at the highest rate in the coming years.
According to the 2017 World Robotics Report, more than 1.7 million new industrial robots will be installed worldwide by 2020, paving the way for increasingly flexible automation. Without a doubt, it is an indication that we are moving towards an increasingly connected world where machines and intelligent automation systems will revolutionize professional life.
IoT, ALONG WITH OTHER DATA SOURCES
as a CRM or ERP will be in charge of providing the data. The AI will be in charge of processing and converting them into information, while blockchain will be in charge of storing them in a way that ensures their reliability
The truth is that this is not a new issue. Since the 1960s, it has been common for companies in the automotive sector to see industrial processes supported by automatons. However, artificial intelligence and everything that surrounds automation related to Industria 4.0 has brought them back to the playing field in the different areas of the company.
- The productive area will be the area where the presence of robotics will be most noticeable, where its presence will increase notably in the next few years in spite of having been in the industry for years. Companies have been able to find new competitive advantages in industrial processes, supported by robotics and Internet of Things (IoT) sensors, which -- thanks to its combination with artificial intelligence -- has triggered the presence of robots in the production processes of companies.
- In the commercial field, the application of robotics is still in a very early stage of prototype testing and field trials. The use of drones in logistics services is perhaps the most tangible exploitation, but it is still in a very experimental phase, far from being adopted as the main option when shipping goods.
- In the financial field, its use in the company is also testimonial. There are functional prototypes, for example, in Shanghai, where the first bank office with robots instead of humans was born, but we are still far from being widely used and served by robots, despite the great advance of Artificial Intelligence (AI).
- As far as the labor force is concerned, it is perhaps, along with the productive sphere, the main one affected by robotics. Human beings will be displaced towards tasks that can provide greater intellectual value, leaving the more tedious and repetitive tasks of the production chains to robots.
IoT
It is a concept that refers to a digital interconnection of everyday objects with the Internet. It is a revolution in the relationships between objects and people, and even directly between objects, which are connected to each other and to the Internet, and offer data in real time. To talk about the implementation of IoT, it is necessary to talk about 5G connections, which will be essential for its development by providing millions of sensors, devices and all kinds of appliances, as well as the ability to connect to the Internet, thus overcoming the current barriers of transmission (especially reducing latency) and energy, since these are the main drawback so far for which it has not been massively adopted.
- In the production area, the connectivity of a multitude of sensors in the robotic elements will boost the speed and efficiency in the supply chains. It will allow you to detect bottlenecks, efficiently measure each production process and better manage inventories.
It will be one of the sources of information that the AI will take advantage of to carry out analysis and convert the data into information, which can be interpreted by a human or by another robot.
- In the commercial field, the value proposals related to logistics are already a reality. By installing IoT devices in sea containers, companies are able to monitor their cargoes seamlessly anywhere in the world, as the devices are able to automatically recognize local standard radio frequencies that are adapting to them.
- These devices, in addition to serving as trackers, also have access to a data analysis platform in order to provide all skateholders (stevedores, transporters, receivers, shipping companies, etc.) with accurate data on the situation of the container at all times, which allows to speed up the supply chain and the quality of service offered to the customer. After the first investigations, it was concluded that this would reduce the maritime inventory by 10% and increase the ETA (estimated time of arrival of shipments) by 40%.
- As for the workforce, there is a great opportunity to measure the performance of workers with the sensors in order to improve work performance. If the sensor data is processed by an artificial intelligence algorithm, which in turn writes a transaction in a blockchain network on the worker's unique digital identifier using a SmartContract, we could objectively evaluate each member of the company based on objective and totally reliable data.